Data types
are attributes that specify the type of data an object can hold.
GIS uses three main data types:
1) Vector2) Raster
3) Tabular
Data formats
are specific or preferred file extensions for sharing, re-use, and preserving data.
Vector data includes formats like shapefiles (.shp).
Shapefiles are GIS-specific data formats used in both proprietary and open-source software.
They come in three types of geometries - points, lines, and polygons.
Raster data stores information in a grid of cells, where each cell holds a value.
Examples include GeoTIFF, TIFF, JPG or DEM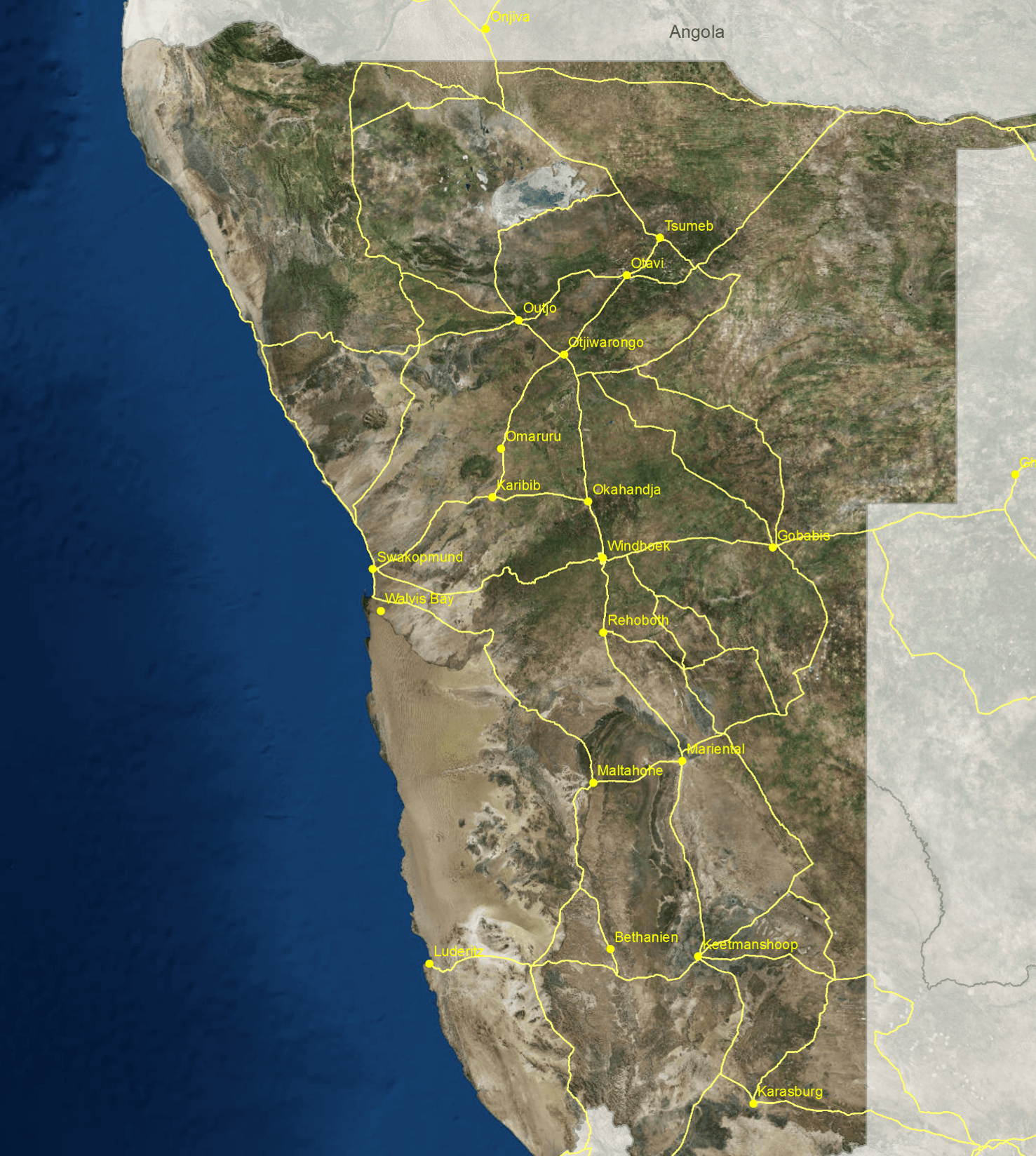
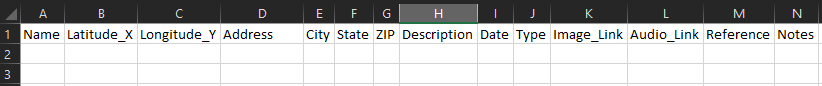
Tabular data is stored as columns and rows.
You can read-in stand-alone tables, or geocode addresses and lat/long coordinates.
The most common formats you’ll work with are .txt and .csv
Previous submodule:
QGIS Examples